Stroke and its types | Stroke is a loss of brain function caused by the interruption of blood flow to the brain area. If blood flow is stopped for longer than a few seconds, the brain tissue cells are not getting the nutrients and oxygen can die and cause permanent damage to brain function.
The most common signs of a stroke is sudden weakness of the face, arm or leg, most often on one side of the body. Other warning signs may include:
Sudden numbness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
Confusion, sudden trouble speaking or understanding speech
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
Sudden severe headache without known cause.
Signs of a stroke depend on the affected side of the brain, parts of the brain affected, and the extent of brain injury. Therefore, each person may have warning signs of stroke are different. Stroke can cause headaches, or perhaps not at all painful.
There are two main types of stroke:
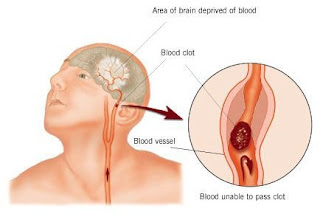
1. Ischemic strokeIschemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain is blocked. This types stroke is the most common (about 90% of strokes are ischemic).
Conditions underlying ischemic stroke is the accumulation of fat that lines the walls of the blood vessels (called atherosclerosis). Cholesterol, homocysteine and other substances can be attached to the walls of arteries, forming a sticky substance called plaque. Over time, plaque builds up. It is often difficult to keep the blood flowing properly and cause a blood clot (thrombus).
Ischemic stroke is distinguished by causing blockage of arteries:
- Thrombotic stroke. Blockages caused by thrombus that develops in the arteries of the brain that is already very narrow.
- Embolic Stroke. Blockages caused by thrombus, air bubble or fat fractions are formed in other body parts, such as the heart and the aorta in the chest and neck, which is carried by the flow of blood to the brain.
2. Hemorrhagic stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke caused by a blood vessel that leaks or ruptures within or around the brain that block the blood supply to the brain tissue in question. In addition, it flooded and compresses the surrounding brain tissue that interfere with or disable the function.
Two types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage. Intracerebral hemorrhage is bleeding in the brain caused by trauma (brain injury) or abnormalities of the blood vessels (aneurysm or angioma). If it is not caused by one of these conditions, most often due to chronic high blood pressure. Intracerebral hemorrhage accounts for approximately 10% of all strokes, but it has the highest percentage of deaths due to stroke.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the subarachnoid space, the space between the inner layer (Pia mater) and middle layer (arachnoid mater) of the tissue lining of the brain (meninges). The most common cause is rupture of the bulge (aneurysm) in the arteries. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a serious medical emergency that can cause permanent disability or death. Stroke is also the only type of stroke is more common in women than in men.
